
×
















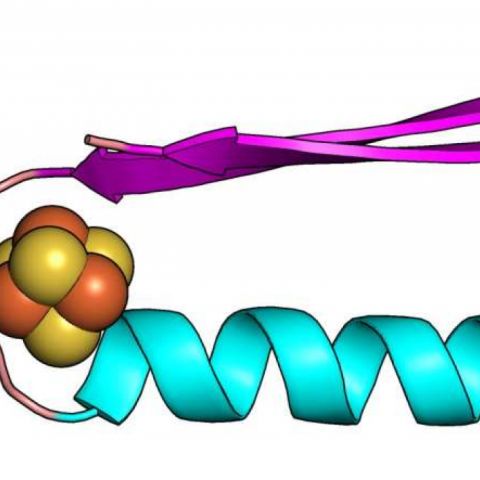




























































































































































Apoptosis is a process that causes cell death. It can go awry in cancer cells, sustaining the disease. Scientists at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital have captured the structure of BAK, a protein that triggers apoptosis. They have shown how BAK autoactivates, essentially turning itself on. Understanding how apoptosis is triggered can lead to drugs that kill cancer cells. The findings were published online today in Nature Communications.
Apoptosis is kick-started by proteins, including BAK, that form pores on the membrane of mitochondria. BAK has to be turned on to work, but the activation process is brief and elusive. BAK can be turned on by either direct activation or autoactivation. Direct activation is a well-studied process where proteins such as BID and BIM turn on BAK. Autoactivation is a less understood process where an active BAK molecule turns on an inactive one.
"Our work shows how BAK autoactivates," said corresponding author Tudor Moldoveanu, Ph.D., St. Jude Departments of Structural Biology and Chemical Biology and Therapeutics. "Once an active BAK is produced through direct activation by BID or BIM, which are upstream activators, then that active BAK can go and turn on dormant BAK."

Apoptosis is a process that causes cell death. It can go awry in cancer cells, sustaining the disease. Scientists at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital have captured the structure of BAK, a protein that triggers apoptosis. They have shown how BAK autoactivates, essentially turning itself on. Understanding how apoptosis is triggered can lead to drugs that kill cancer cells. The findings were published online today in Nature Communications.
Apoptosis is kick-started by proteins, including BAK, that form pores on the membrane of mitochondria. BAK has to be turned on to work, but the activation process is brief and elusive. BAK can be turned on by either direct activation or autoactivation. Direct activation is a well-studied process where proteins such as BID and BIM turn on BAK. Autoactivation is a less understood process where an active BAK molecule turns on an inactive one.
"Our work shows how BAK autoactivates," said corresponding author Tudor Moldoveanu, Ph.D., St. Jude Departments of Structural Biology and Chemical Biology and Therapeutics. "Once an active BAK is produced through direct activation by BID or BIM, which are upstream activators, then that active BAK can go and turn on dormant BAK."
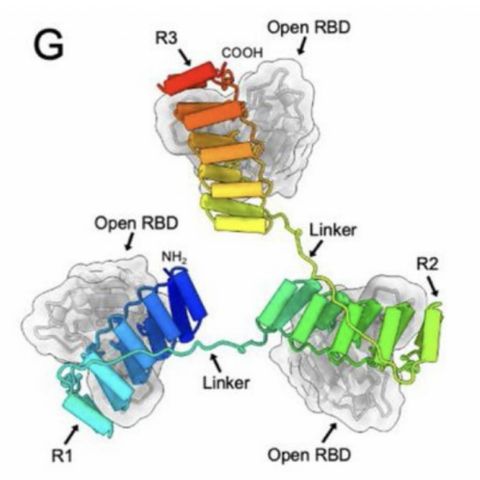
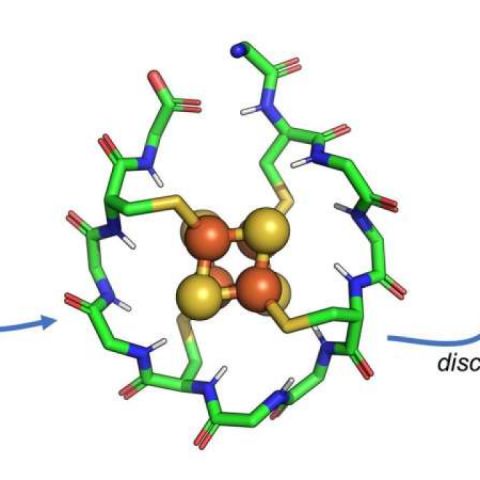
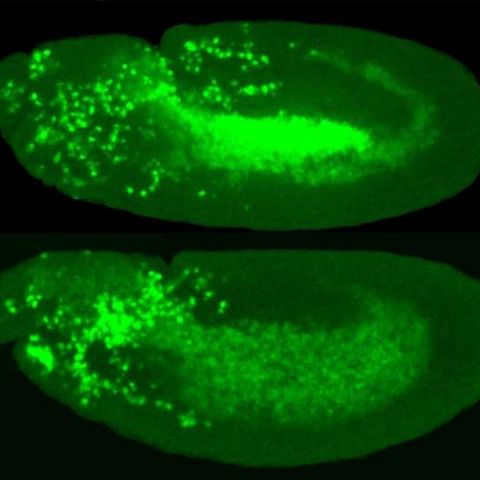
The researchers used structural biology, biochemistry and cellular assays to determine the mechanism of BAK autoactivation. They produced the first crystal structure for autoactivated BAK. The structure revealed that conformational (shape) changes destabilize an important inhibitory helix. This destabilization underlies a common mechanism of BAK activation by BID, BIM and BAK.
The BH3 domain is a ligand already known to be involved in direct activation. The researchers identified positions on the BH3 domain that were beneficial for activating or inhibiting BAK. They determined crystal structures that show how BH3 ligands with high affinity (strong binding) can activate and inhibit BAK. Ultimately, the work suggests that both the direct activation and autoactivation processes cooperate to trigger apoptosis in cells.